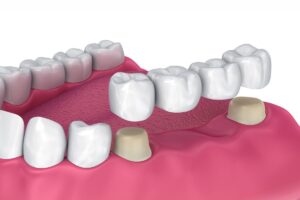
To fabricate, Fixed Partial Denture (FPD), commonly known as bridge, the dentist needs to take support from
the adjacent teeth structure. In case of absence of supporting adjacent teeth, the dentist places an
implant. So to understand properly, these adjacent teeth or implants serve as the pillars of the bridge.
Scientifically the dentist call these pillars as abutment. The selection of abutment in terms of location
and characteristics are very crucial in long term success of the FPD. The following points are considered
by the dentists before placing on a fixed prosthesis.
1. Location of the abutment/adjacent teeth
2. Size and length of the edentulous (the place of missing teeth) area
3. Structural condition of the adjacent teeth – If grossly carious or have higher attrition.
4. Root Configuration – The ideal root for the fpd should have higher width (labiolingual), more
irregular curvature and longer roots. For tooth like molars, the multiple roots works like miracle.
5. Crown Root Ratio – One of the most vital analysis the dentists do is the crown root ratio. The
clinical crown is the tooth part that is exposed from the alveolar bone. A negative crown root
ratio or 2:3 is a good to go for. Even 1:1 is acceptable but above that will definitely create
problem in long term success
6. Alveolar / surround bone support of the tooth – The dentist always consider the bone quality of
the area.
7. Periodontal Ligament – PDL is the soft elastic like tissue that attached the tooth with the bone.
Any chronic inflammation of the PDL can be a hindrance in the FPD
8. Understanding the pulpal condition – The pulpal condition of the abutments to be assessed.
Unrestored teeth are preferred, however if there are signs of caries or any other pathologies, it
should be treated before the FPD.
Grossly it should be understood that the number of abutments needs to be increased if the missing area
is longer. In case of absence of teeth at the back region without any last tooth , dental implants are must to restore the biting balance.
